This is a versatile mineral known for its brightness, opacity, and durability, making it valuable across numerous industries. Titanium dioxide uses range from paints and plastics to cosmetics and ceramics, featuring prominently in many products encountered daily.
This compound’s popularity arises from its unique properties, including exceptional whiteness, resistance to UV light, and chemical stability. These characteristics make it a key component in traditional materials and innovative applications like photocatalysis and self-cleaning surfaces.
This article looks at the ways titanium dioxide is used in various industries, its contributions to everyday products, and the challenges it faces as industries adapt to new demands.
Pigments in Paints and Coatings
Titanium dioxide is widely used in the paint and coatings industry as one of the most effective white pigments. Its ability to scatter light improves the opacity and brightness of paints, ensuring strong coverage even with thin layers. This makes it a key component for creating vibrant, long-lasting finishes in both residential and commercial settings.
Its durability also plays a significant role in protecting surfaces from UV damage, helping to maintain colour over time. These properties make titanium dioxide an important ingredient in architectural paints, automotive finishes, and industrial coatings, where consistent performance is essential.
For architectural applications, titanium dioxide is needed in interior and exterior wall paints. It provides the bright, clean finish desired in homes and offices, while also offering the durability to withstand exposure to sunlight and weather conditions. In automotive applications, it is used in car paints to achieve a high-gloss finish and to maintain colour vibrancy even after prolonged exposure to harsh sunlight, road debris, and temperature changes.
From walls to vehicles, titanium dioxide helps create surfaces that are visually appealing, durable, and capable of withstanding the demands of both everyday use and challenging environments.
Plastics

This compound’s UV resistance helps protect plastics from degradation caused by sunlight, extending the lifespan of outdoor and high-exposure items all while retaining its original colour. This covers things like:
- Packaging materials
- Automotive parts
- Household goods
- Outdoor furniture
This compound helps create plastics that are not only durable but also visually appealing, maintaining their quality and appearance over time. By improving resistance to UV light and wear, it contributes to longer-lasting products that retain their aesthetic appeal even in challenging environments.
Paper
The light-scattering properties of titanium dioxide help create a clean and vivid appearance, which is particularly important for high-quality printing and packaging applications. In speciality papers, such as those used for magazines, labels, and luxury packaging it increases sharp visuals and crisp text by improving the contrast and printability of the surface. Reducing the transparency of the paper also helps minimise ink bleed, which is critical for detailed graphics and multi-colour prints.
Ceramics

This compound is particularly valued in glazing applications, where it enhances the visual appeal of decorative ceramics, tiles, and sanitaryware by creating a uniform, polished finish.
Its role extends beyond aesthetics. Titanium dioxide contributes to the durability of ceramics, making them more resistant to wear, heat, and chemical exposure. This makes it an essential component in products like bathroom fixtures, kitchen tiles, and industrial ceramics, where both function and appearance are critical.
Recent innovations in ceramic manufacturing have leveraged titanium dioxide to improve energy efficiency and production quality. Its use in advanced formulations enables the creation of thinner, stronger materials while maintaining performance standards.
Floor Coverings
When used for vinyl flooring, it increases colour vibrancy and patterns remain crisp and visually appealing. Its light-scattering properties also contribute to creating even, consistent tones across large surfaces.
Durability is another key benefit. Titanium dioxide provides UV resistance, which helps prevent fading and discolouration caused by sunlight exposure. This makes it particularly important for flooring in high-traffic areas and spaces with significant natural light, such as offices, retail environments, and residential interiors.
From carpets to tiles, titanium dioxide supports the development of materials that are both long-lasting and visually striking. However, the environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of these materials, particularly those containing titanium dioxide, remains a challenge as the industry seeks more sustainable solutions.
Photocatalysts
Titanium dioxide is a key material in photocatalysis, where it is used to drive chemical reactions under light exposure. One of its most important applications is in environmental purification, such as breaking down pollutants in air and water. Self-cleaning surfaces, including windows and building facades, often incorporate titanium dioxide to degrade organic dirt and reduce maintenance needs.
In air purification, titanium dioxide helps to remove harmful substances like nitrogen oxides, which are common in urban environments. Similarly, in water treatment, it plays a role in breaking down contaminants, contributing to cleaner and safer resources.
Emerging technologies are also exploring its use in renewable energy, such as developing more efficient solar cells and energy storage systems. However, the effectiveness of titanium dioxide in some photocatalytic processes is limited by its dependence on UV light, which accounts for only a small portion of natural sunlight. Research is ongoing to improve its performance under visible light and expand its potential applications.
Sun Creams
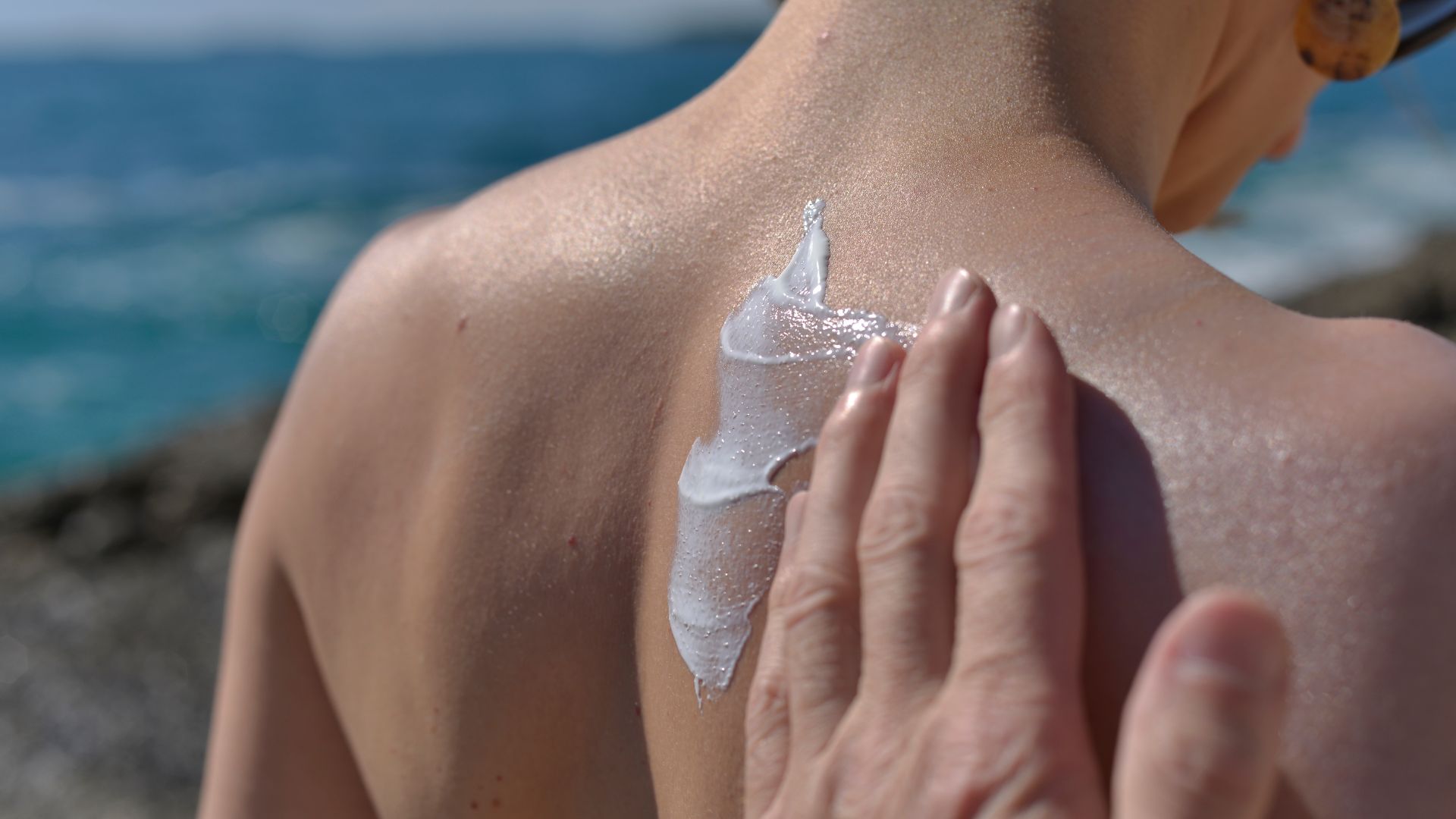
Titanium dioxide is a widely used ingredient in sun creams, valued for its ability to provide broad-spectrum UV protection. Unlike chemical sunscreens that absorb UV radiation, titanium dioxide acts as a physical blocker, reflecting and scattering harmful rays away from the skin. This makes it particularly effective in protecting against both UVA and UVB radiation.
One of its key benefits is its non-irritating nature, making it a preferred choice for sensitive skin formulations. It is also commonly included in natural or mineral-based sunscreens, where consumers seek products free from synthetic chemicals.
Food Colouring
This chemical has been widely used as a bright white food colouring, improving the visual appeal of a broad range of products. It adds to the appearance of items such as confectionery, dairy products, and baked goods, making them more attractive to consumers. Its use helps maintain consistency across batches, which is particularly important for the quality of mass-produced foods.
Titanium dioxide’s unique properties have made it indispensable across a range of industries, from paints and plastics to cosmetics and ceramics. Its ability to improve the appearance and performance of everyday products underscores its versatility and importance.
However, challenges around sustainability and regulatory concerns are prompting industries to rethink how this compound is used. As innovation continues, titanium dioxide will remain central to both traditional applications and emerging technologies, shaping the future of materials science.